JAVA Image Guide
- This document applies to images of version
>=3.0. For images of version<=2.x, please refer to the 2.x documentation
By default, network access is turned off to a ECS instance. You can specify rules in a security group that allows access from an IP address range, port, or ECS security group.
You must specify port numbers (for TCP):
- 22 (ssh)
- 80 (http)
- 443 (https)
Alibabacloud Security groups document URL: Alibabacloud Security group
Image environment description
Image version description
Software version
- Nginx1.28
- OpenJDK17.0, OpenJDK11.0, OpenJDK1.8
- MySQL8.0
- Redis7.4
- Memcached1.6
- Jemalloc5.3.0
Image Feature
- Source compiler installation, download the latest and most stable version from the official, security optimization
- Providing multiple JDK versions (OpenJDK17.0, OpenJDK11.0, OpenJDK1.8)
- Jemalloc optimize Nginx, MySQL/MariaDB
- Providing add a virtual host script, include Let's Encrypt SSL certificate
- Provide Nginx, MySQL/MariaDB, Redis, Memcached, phpMyAdmin upgrade script
- Provide local backup and remote backup (rsync between servers), Alibaba cloud OSS backup(Intranet) script
Application installation directories
Install directory
- Nginx:
/usr/local/nginx - Tomcat:
/usr/local/tomcat - JDK:
/usr/lib/jvm - MySQL:
/usr/local/mysqlor MariaDB/usr/local/mariadb - Redis:
/usr/local/redis - Memcached:
/usr/local/memcached
Data directory
- Database data directory:
/data/mysqlor/data/mariadb - Webroot directory:
/data/wwwroot/www.example.com - Web logs directory:
/data/wwwlogs - Web Context document root:
/data/wwwroot/default - Index demo url:
http://<Public net IP>
How do use scripts to optimize the parameters
Because this image was build based on 1 Core 1G ECS,the configuration and parameters for MySQL/MariaDB,PHP are original without any change, highly recommended If this is not the case, run the following optimization script:
sudo /root/weiliu/optimize.sh
- Do not execute bash optimize.sh (or sh) for documentation commands
- It may take 1 minute to wait, please do not interrupt
- This script will automatically optimize Nginx, MySQL, JVM and other parameters according to the system configuration
[root@WeiLiu ~]# sudo /root/weiliu/optimize.sh
Change JDK Version
sudo /root/weiliu/change_jdk_version.sh
[root@WeiLiu ~]# sudo /root/weiliu/change_jdk_version.sh
#######################################################################
# Change your JDK version #
#######################################################################
Current JDK Version: 1.8.0_352
Please select a version of the JDK:
1. openjdk-8-jdk
2. openjdk-11-jdk
3. openjdk-17-jdk
Please input a number:(Default 1 press Enter) 2
You have successfully changed to openjdk-11-jdk
[root@WeiLiu ~]# java -version
openjdk version "11.0.17" 2022-10-18 LTS
OpenJDK Runtime Environment (Red_Hat-11.0.17.0.8-2.el8_6) (build 11.0.17+8-LTS)
OpenJDK 64-Bit Server VM (Red_Hat-11.0.17.0.8-2.el8_6) (build 11.0.17+8-LTS, mixed mode, sharing)
Migrating website from os disk to data disk
If you purchased a data disk (And only one data disk), It is recommended to mount the data disk first, the site content, database storage data cloud disk, If there is no purchase data cloud disk Ignore the tutorial!
sudo /root/weiliu/move_auto_fdisk.sh
[root@WeiLiu ~]# sudo /root/weiliu/move_auto_fdisk.sh
#######################################################################
# Auto fdisk #
#######################################################################
Step 1.No lock file, begin to create lock file and continue
Step 2.Begin to check free disk
You have a free disk, Now will fdisk it and mount it
This system have free disk :
/dev/vdb
Step 3.Begin to fdisk free disk
Step 4.Begin to make directory
Step 5.Begin to write configuration to /etc/fstab and mount device
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
devtmpfs 1.8G 0 1.8G 0% /dev
tmpfs 1.8G 24K 1.8G 1% /dev/shm
tmpfs 1.8G 432K 1.8G 1% /run
tmpfs 1.8G 0 1.8G 0% /sys/fs/cgroup
/dev/vda1 50G 8.8G 39G 19% /
tmpfs 361M 0 361M 0% /run/user/0
/dev/vdb1 9.8G 37M 9.3G 1% /data
DB Management
Display DB default root password
sudo grep dbrootpwd /root/weiliu/options.conf
[root@WeiLiu ~]# sudo grep dbrootpwd /root/weiliu/options.conf
dbrootpwd='A0R3Ru5Z' #Tip: Random Password
Change DB root password
sudo /root/weiliu/reset_db_root_password.sh
[root@WeiLiu ~]# sudo grep dbrootpwd /root/weiliu/options.conf
dbrootpwd='A0R3Ru5Z'
[root@WeiLiu ~]# sudo /root/weiliu/reset_db_root_password.sh
#######################################################################
# Reset Database root password #
#######################################################################
Please input the root password of database: VrTN4k5PYHsw
Password reset succesfully!
The new password: VrTN4k5PYHsw
[root@WeiLiu ~]# mysql -uroot -p
Enter password: #Tip: Enter the database root password, it will not be displayed on the screen when entering
MySQL [(none)]>
Create a database
e.g.: create a database name weiliu
mysql -uroot –p
Enter password:
MySQL [(none)]> create database weiliu;
MySQL [(none)]> show databases;
MySQL [(none)]> exit;
[root@WeiLiu ~]# mysql -uroot -p
Enter password:
MySQL [(none)]> create database weiliu;
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec)
MySQL [(none)]> show databases;
+--------------------+
| Database |
+--------------------+
| information_schema |
| mysql |
| weiliu |
| performance_schema |
| sys |
+--------------------+
5 rows in set (0.00 sec)
MySQL [(none)]> exit;
Bye
Delete a database
elete a database name weiliu
mysql -uroot –p
Enter password:
MySQL [(none)]> drop database weiliu;
MySQL [(none)]> show databases;
MySQL [(none)]> exit;
[root@WeiLiu ~]# mysql -uroot -p
Enter password:
MySQL [(none)]> show databases;
+--------------------+
| Database |
+--------------------+
| information_schema |
| mysql |
| weiliu |
| performance_schema |
| sys |
+--------------------+
5 rows in set (0.00 sec)
MySQL [(none)]> drop database weiliu;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
MySQL [(none)]> show databases;
+--------------------+
| Database |
+--------------------+
| information_schema |
| mysql |
| performance_schema |
| sys |
+--------------------+
4 rows in set (0.00 sec)
MySQL [(none)]> exit;
Bye
Create a database user
For security purposes, we usually create a unique database connection account for each web application(Account name can not be root).
E.g: Add a user named: db_user,password: 123456, Authorization for the localhost to the db_name database all permissions, the commands are as follows:
mysql -uroot -p #Tip: Enter mysql console
Enter password: #Tip: Enter mysql root password
MySQL [(none)]> create user db_user@'localhost' identified by 'db_pass';
MySQL [(none)]> grant all privileges on db_name.* to db_user@'localhost';
MySQL [(none)]> flush privileges;
MySQL [(none)]> exit; #Tip: quit mysql console, Notice the semicolon at the end
[root@WeiLiu ~]# mysql -uroot -p
Enter password:
MySQL [(none)]> create user db_user@'localhost' identified by 'db_pass';
Query OK, 0 rows affected, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
MySQL [(none)]> grant all privileges on db_name.* to db_user@'localhost';
Query OK, 0 rows affected, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
MySQL [(none)]> flush privileges;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
MySQL [(none)]> exit;
Bye
How to setup a remote DB connection
For security reasons, Only allows the cloud host localhost to connect to the database,if you need a remote connection to the database,the following operations are required:
The cloud host security group port, and grant authorized users are indispensable.
1. You must open port 3306 for Security groups
Security groups document URL: Alibabacloud Security group
2. Database authorization
Create a new account for remote connection (the account name cannot be root, the remote database account is not recommended to be root, if you need root remote connection, please update the corresponding row of the mysql.user table).
e.g.: Add a user named db_user, password db_pass,Authorized as % (% Represents all ip can connect, you can set the designated ip) db_name database all authority, the commands are as follows
mysql -uroot -p
MySQL [(none)]> create user db_user@'localhost' identified by 'db_pass';
MySQL [(none)]> grant all privileges on db_name.* to db_user@'localhost';
MySQL [(none)]> flush privileges;
MySQL [(none)]> exit;
[root@WeiLiu ~]# mysql -uroot -p
Enter password:
MySQL [(none)]> create user db_user@'localhost' identified by 'db_pass';
Query OK, 0 rows affected, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
MySQL [(none)]> grant all privileges on db_name.* to db_user@'localhost';
Query OK, 0 rows affected, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
MySQL [(none)]> flush privileges;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
MySQL [(none)]> exit;
Bye
How to manage virtual host
How to add a virtual host
sudo /root/weiliu/vhost.sh
[root@WeiLiu ~]# sudo /root/weiliu/vhost.sh
#######################################################################
# Setting up virtual hosts on HTTP Server #
#######################################################################
Please choose to use environment:
1. Use php
2. Use java
Please input a number:(Default 1 press Enter) 2
What Are You Doing?
1. Use HTTP Only
2. Use your own SSL Certificate and Key
3. Use Let's Encrypt to Create SSL Certificate and Key
q. Exit
Please input the correct option: 3
Please input domain(example: www.example.com): demo.linuxeye.com
domain=demo.linuxeye.com
Please input the directory for the domain:demo.linuxeye.com :
(Default directory: /data/wwwroot/demo.linuxeye.com):
Virtual Host Directory=/data/wwwroot/demo.linuxeye.com
Create Virtul Host directory......
set permissions of Virtual Host directory......
Do you want to add more domain name? [y/n]: y
Type domainname or IP(example: example.com other.example.com): demo2.linuxeye.com
domain list=demo2.linuxeye.com
Do you want to redirect from demo2.linuxeye.com to demo.linuxeye.com? [y/n]: y
Do you want to redirect all HTTP requests to HTTPS? [y/n]: y
Please select domain cert key length.
Enter one of 2048, 3072, 4096, 8192 will issue a RSA cert.
Enter one of ec-256, ec-384, ec-521 will issue a ECC cert.
Please enter your cert key length (default 2048): 2048
Please enter your email: lj2007331@mail.com
[Sun Oct 30 04:27:06 PM CST 2022] Create account key ok.
[Sun Oct 30 04:27:06 PM CST 2022] No EAB credentials found for ZeroSSL, let's get one
[Sun Oct 30 04:27:13 PM CST 2022] Registering account: https://acme.zerossl.com/v2/DV90
[Sun Oct 30 04:27:15 PM CST 2022] Could not get nonce, let's try again.
[Sun Oct 30 04:27:39 PM CST 2022] Registered
[Sun Oct 30 04:27:39 PM CST 2022] ACCOUNT_THUMBPRINT='LMG4Elq-AFm-IH17QAk3yjmp-8TNoxi__gWTIIT1tzY'
....
[Sun Oct 30 04:28:20 PM CST 2022] Cert success.
nginx: the configuration file /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf syntax is ok
nginx: configuration file /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf test is successful
Do you want to add hotlink protection? [y/n]: n
Allow Rewrite rule? [y/n]: y
Please input the rewrite of programme :
wordpress,opencart,magento2,drupal,joomla,codeigniter,laravel
thinkphp,pathinfo,discuz,typecho,ecshop,nextcloud,zblog,whmcs rewrite was exist.
(Default rewrite: other): linuxeye
You choose rewrite=linuxeye
Allow Nginx/Tengine/OpenResty access_log? [y/n]: y
You access log file=/data/wwwlogs/demo.linuxeye.com_nginx.log
nginx: the configuration file /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf syntax is ok
nginx: configuration file /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf test is successful
Reload Nginx......
#######################################################################
# Setting up virtual hosts on HTTP Server #
#######################################################################
Your domain: demo.linuxeye.com
Virtualhost conf: /usr/local/nginx/conf/vhost/demo.linuxeye.com.conf
Tomcat Virtualhost conf: /usr/local/tomcat/conf/vhost/demo.linuxeye.com.xml
Directory of: /data/wwwroot/demo.linuxeye.com
Rewrite rule: /usr/local/nginx/conf/rewrite/linuxeye.conf
Let's Encrypt SSL Certificate:/usr/local/nginx/conf/ssl/demo.linuxeye.com.crt
SSL Private Key: /usr/local/nginx/conf/ssl/demo.linuxeye.com.key
The above Directory of is the website root directory (/data/wwwroot/demo.linuxeye.com), which will be automatically created after the script is executed. Please upload the code to this directory when deploying the website (directory, subdirectory and file permissions are: www).
- Nginx the configuration file path:
/usr/local/nginx/conf/vhost/demo.linuxeye.com.conf - Nginx the rewrite file path:
/usr/local/nginx/conf/rewrite/linuxeye.conf - Tomcat the configuration file path:
/usr/local/tomcat/conf/vhost/demo.linuxeye.com.xml
How to delete a virtual host
sudo /root/weiliu/vhost.sh --del
[root@WeiLiu ~]# sudo /root/weiliu/vhost.sh --del
#######################################################################
# Setting up virtual hosts on HTTP Server #
#######################################################################
Virtualhost list:
demo1.linuxeye.com demo.linuxeye.com www.linuxeye.com
Please input a domain you want to delete: demo.linuxeye.com
Do you want to delete Virtul Host directory? [y/n]: y
Press Ctrl+c to cancel or Press any key to continue...
Domain: demo.linuxeye.com has been deleted.
How to Connect to SFTP Server Using Filezilla
Filezilla PC Client
Download link: https://filezilla-project.org/download.php
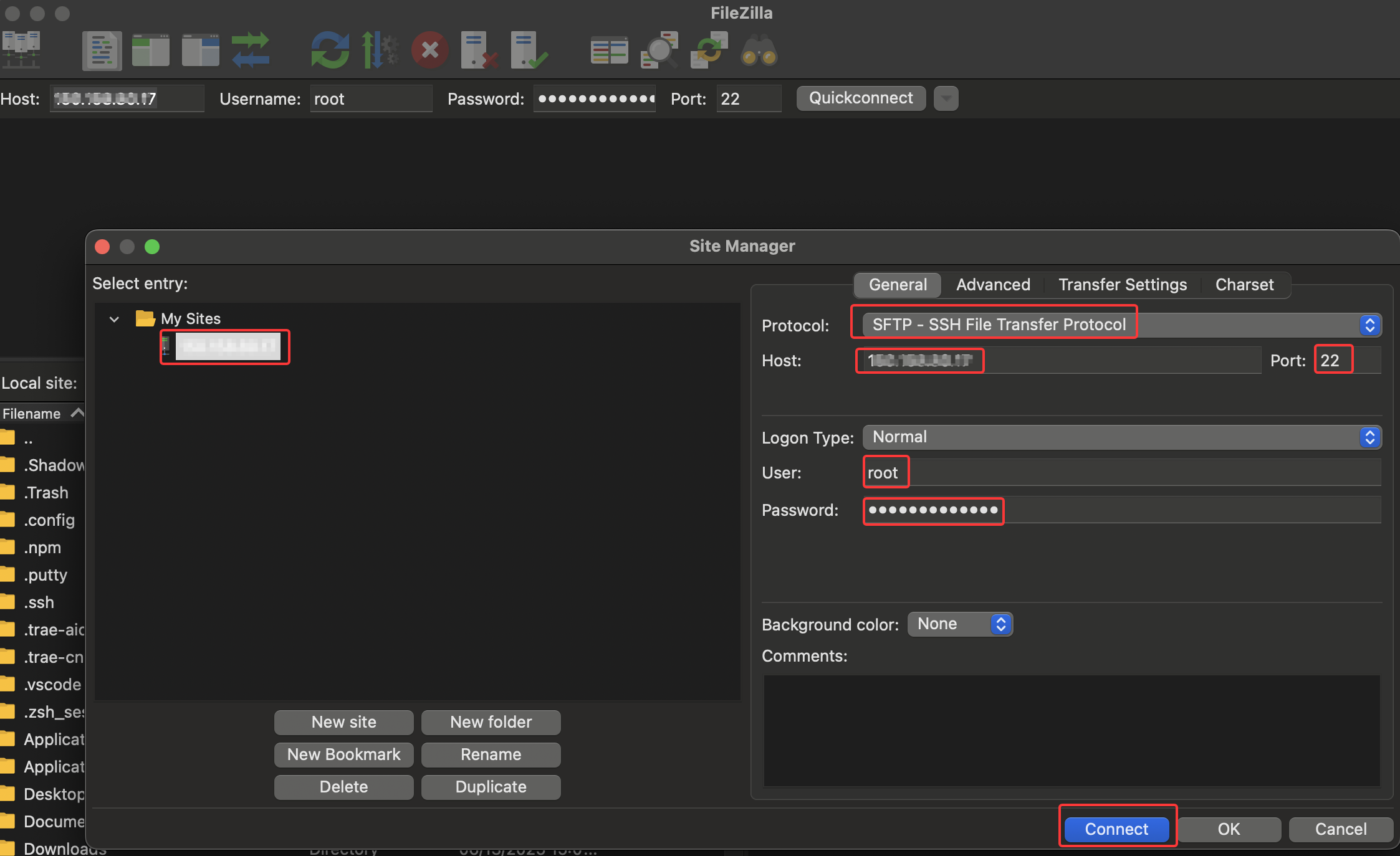
Steps to Connect to SFTP Server
- After opening the Filezilla client, click "File" -> "Site Manager" in the top menu bar
- Click the "New Site" button and enter a site name (e.g., "My SFTP Server")
- Select "SFTP - SSH File Transfer Protocol" from the "Protocol" dropdown menu
- Enter the host address (e.g.,
server public IP address), username (e.g.,root), and password (server SSH login password) - The default port is 22 (SFTP default port), please enter the actual port number if a custom port is needed
- Click the "Connect" button. For the first connection, a server key confirmation window will pop up, click "OK" to establish the connection
As shown below:
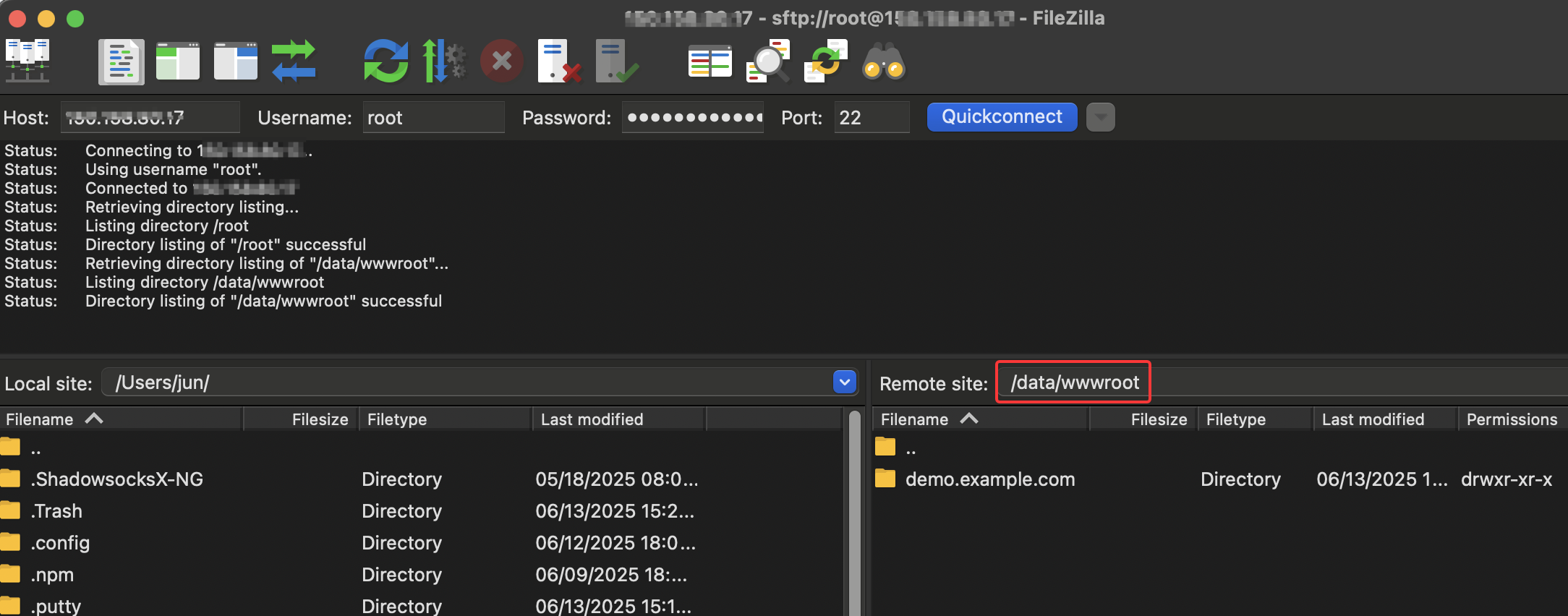
Upload Files to Website Root Directory
Please set the upload file path to /data/wwwroot, upload to the bound website root directory, such as /data/wwwroot/demo.example.com
As shown below:
About Website Root Directory Permissions
If you use Filezilla SFTP with the root user to upload website data to the /data/wwwroot/You bond domain/ directory, the files and folders will be owned by the root user/group, while Nginx/Tomcat runs as the www user. You need to correct the website root directory permissions by executing the following command:
chown -R www:www /data/wwwroot/
Website root directory permissions should follow: both user and group should be www, file permissions 644, folder permissions 755
Refer to 《About site root permissions》
How to backup
Backup Set Parameters
sudo /root/weiliu/backup_setup.sh
[root@WeiLiu ~]# sudo /root/weiliu/backup_setup.sh
#######################################################################
# Setup the backup parameters #
#######################################################################
Please select your backup destination:
1. Localhost
2. Remote host
3. Aliyun OSS
4. Qcloud COS
5. UPYUN
6. QINIU
7. Amazon S3
8. Dropbox
Please input numbers:(Default 1 press Enter) 1
Please select your backup content:
1. Only Database
2. Only Website
3. Database and Website
Please input a number:(Default 1 press Enter) 1
Please enter the directory for save the backup file:
(Default directory: /data/backup):
Please enter a valid backup number of days:
(Default days: 5): 10
Please enter one or more name for database, separate multiple database names with commas:
(Default database: linuxeye,weiliu) linuxeye,weiliu
You have to backup the content:
Database: linuxeye,weiliu
Perform the backup immediately
sudo /root/weiliu/backup.sh
** Setup scheduled tasks to automatically schedule backup **
sudo echo '0 1 * * * sudo /root/weiliu/backup.sh > /dev/null 2>&1' >> /var/spool/cron/root
Do not repeat the above command.
** View the local backup **
ls -l /data/backup
[root@WeiLiu ~]# ls -l /data/backup/
total 12
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 637 Oct 30 19:15 DB_linuxeye_20221030_191506.tgz
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 258 Oct 30 19:15 db.log
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 641 Oct 30 19:15 DB_weiliu_20221030_191506.tgz
If you set up remote cloud storage backup, view a cloud storage
** Login to a cloud management console **
As shown below:
如何管理服务
- Systemd
- Service
systemctl {start|stop|status|restart|reload} nginx
Change the Nginx configuration file, it is recommended to reload, ie systemctl reload nginx
systemctl {start|stop|status|restart} tomcat
systemctl {start|stop|restart|status} mysqld
systemctl {start|stop|status|restart|reload} redis-server
systemctl {start|stop|status|restart|reload} memcached
service nginx {start|stop|status|restart|reload}
Change the Nginx configuration file, it is recommended to reload, ie service nginx reload
service tomcat {start|stop|status|restart}
service mysqld {start|stop|restart|status}
service redis-server {start|stop|status|restart|reload}
service memcached {start|stop|status|restart|reload}
How to upgrade
sudo /root/weiliu/upgrade.sh
[root@WeiLiu ~]# sudo /root/weiliu/upgrade.sh -h
#######################################################################
# Upgrade Software versions #
#######################################################################
Usage: ./upgrade.sh command ...[version]....
--help, -h Show this help message
--nginx [version] Upgrade Nginx
--tengine [version] Upgrade Tengine
--openresty [version] Upgrade OpenResty
--apache [version] Upgrade Apache
--tomcat [version] Upgrade Tomcat
--db [version] Upgrade MySQL/MariaDB/Percona
--php [version] Upgrade PHP
--redis [version] Upgrade Redis
--memcached [version] Upgrade Memcached
--phpmyadmin [version] Upgrade phpMyAdmin
--script Upgrade scripts latest
--acme.sh Upgrade acme.sh latest
[root@WeiLiu ~]# sudo /root/weiliu/upgrade.sh
#######################################################################
# Upgrade Software versions #
#######################################################################
What Are You Doing?
1. Upgrade Nginx/Tengine/OpenResty
2. Upgrade Apache
3. Upgrade Tomcat
4. Upgrade MySQL/MariaDB/Percona
5. Upgrade PHP
6. Upgrade Redis
7. Upgrade Memcached
8. Upgrade phpMyAdmin
9. Upgrade scripts latest
10. Upgrade acme.sh latest
q. Exit
Please input the correct option: q
Add addons component
sudo /root/weiliu/addons.sh
Execute sudo /root/weiliu/addons.sh --help to view supported parameters
[root@WeiLiu ~]# sudo /root/weiliu/addons.sh -h
#######################################################################
# Install/Uninstall Extensions #
#######################################################################
Usage: /root/weiliu/addons.sh command ...
--help, -h Show this help message
--install, -i Install
--uninstall, -u Uninstall
--composer Composer
--fail2ban Fail2ban
--ngx_lua_waf Ngx_lua_waf
[root@WeiLiu ~]# sudo /root/weiliu/addons.sh
#######################################################################
# Install/Uninstall Extensions #
#######################################################################
What Are You Doing?
1. Install/Uninstall PHP Composer
2. Install/Uninstall fail2ban
3. Install/Uninstall ngx_lua_waf
q. Exit
Please input the correct option: 3
Please select an action:
1. install
2. uninstall
Please input a number:(Default 1 press Enter) 1
How to uninstall
sudo /root/weiliu/uninstall.sh
Some items can be uninstalled separately. For example, if the database uses a cloud vendor RDS, the database can be uninstalled separately. Pay attention to backing up the data.
[root@WeiLiu ~]# sudo /root/weiliu/uninstall.sh -h
#######################################################################
# Uninstall #
#######################################################################
Usage: ./uninstall.sh command ...[parameters]....
--quiet, -q quiet operation
--all Uninstall All
--web Uninstall Nginx/Tengine/OpenResty/Apache/Tomcat
--mysql Uninstall MySQL/MariaDB/Percona
--postgresql Uninstall PostgreSQL
--mongodb Uninstall MongoDB
--php Uninstall PHP (PATH: /usr/local/php74)
--mphp_ver [53~84] Uninstall another PHP version (PATH: /usr/local/php74${mphp_ver})
--allphp Uninstall all PHP
--phpcache Uninstall PHP opcode cache
--php_extensions [ext name] Uninstall PHP extensions, include zendguardloader,ioncube,
sourceguardian,imagick,gmagick,fileinfo,imap,ldap,calendar,phalcon,
yaf,yar,redis,memcached,memcache,mongodb,swoole,xdebug
--pureftpd Uninstall PureFtpd
--redis Uninstall Redis-server
--memcached Uninstall Memcached-server
--phpmyadmin Uninstall phpMyAdmin
--nodejs Uninstall Nodejs (PATH: /usr/local/node)
[root@WeiLiu ~]# sudo /root/weiliu/uninstall.sh
#######################################################################
# Uninstall #
#######################################################################
What Are You Doing?
0. Uninstall All
1. Uninstall Nginx/Tengine/OpenResty/Apache/Tomcat
2. Uninstall MySQL/MariaDB/Percona
3. Uninstall PostgreSQL
4. Uninstall MongoDB
5. Uninstall all PHP
6. Uninstall PHP opcode cache
7. Uninstall PHP extensions
8. Uninstall PureFtpd
9. Uninstall Redis
10. Uninstall Memcached
11. Uninstall phpMyAdmin
12. Uninstall Nodejs (PATH: /usr/local/node)
q. Exit
Please input the correct option: q
More
How to deploy a java website on a server
- Create the database required for the site,reference《Create a database》
- Add a virtual host,reference 《How to add a virtual host》Create JAVA vhost
- Upload website data to the server, refer to 《How to Connect to SFTP Server Using Filezilla》
- Deploy the code to the site webroot directory
Ftp upload code do not need to modify permissions,default is already www; Download the code in server, you must modify the site root and subdirectories,Directory file permissions are www; If there is a problem with site permissions,Please refer to《About site root permissions》
[root@WeiLiu ~]# ls
demo.war ReadMe
[root@WeiLiu ~]# cd /data/wwwroot/demo.linuxeye.com
[root@WeiLiu demo.linuxeye.com]# jar xf /root/demo.war
[root@WeiLiu demo.linuxeye.com]# ls -l
total 4
drwxr-xr-x 4 root root 4096 Oct 30 19:26 demo
[root@WeiLiu demo.linuxeye.com]# mv demo/* .
[root@WeiLiu demo.linuxeye.com]# rm -rf demo
[root@WeiLiu demo.linuxeye.com]# chown -R www.www ./
[root@WeiLiu demo.linuxeye.com]# systemctl restart tomcat
** Create deploy JAVA website **
The default mirror is static and dynamic separation, that is, nginx handles static resources (JSS, CCC, pictures, etc.), and the rest goes to Tomcat processing.
The default (non binding domain) corresponding to the site root directory /data/wwwroot/default (not webapps), the deployment of code recommendations will pack War (such as example.war, jar xf example.war, unzip: note that permissions must be WWW), the code into the corresponding web site root directory.
- If you upload the code, the directory structure is
/data/wwwroot/default/WEB-INF, and the access address is:http://IP - If you upload the code, the directory structure is:
/data/wwwroot/default/example/WEB-INF, access the web site address is:http://IP/example.
- The war package can also be uploaded to the corresponding web root without decompression, but you must pay attention to access paths and static resource directory issues. If you visit the site, the static loading of resources may be the reason is not, do separate static resources directly with nginx, please confirm whether nginx can find relevant static resources (nginx web site root directory:
/data/wwwroot/default) - If the
vhost.shbinds the domain name, such as www.example.com, the tool automatically generates the corresponding root directory:/data/wwwroot/www.example.com, put the code in this directory. - Tomcat parameter, please modify:
/usr/local/tomcat/bin/setenv.sh
About site root permissions
Webroot permissions to follow::
file 644, folder 755, Permissions Users and groups www
If there is a file permissions problem, execute the following three commands:
chown -R www.www /data/wwwroot/
find /data/wwwroot/ -type d -exec chmod 755 {} \;
find /data/wwwroot/ -type f -exec chmod 644 {} \;
About redis and memcached
- Redis default port:
6379 - Memcached default port:
11211 - default only listen IP:
127.0.0.1
How to increase the maximum memory size of Redis?
vi /usr/local/redis/etc/redis.conf
maxmemory 1024000000 #Unit byte
systemctl restart redis-server
How to increase the maximum memory size of Redis?
vi /lib/systemd/system/memcached.service
Environment=CACHESIZE=256 #Unit MB
systemctl daemon-reload
systemctl restart memcached
Change Redis listening port
vi /usr/local/redis/etc/redis.conf
bind 127.0.0.1 change to bind 0.0.0.0
- Systemd
- Service
systemd is the latest initialization system (init) of the Linux system. Its function is to improve the startup speed of the system, start as few processes as possible, and start as many processes as possible concurrently. The corresponding process management command is systemctl, which is supported by CentOS7 and Ubuntu/Debian. It is recommended to use sytemd to manage services.
systemctl restart redis-server
service The service management method used by the old system, such as CentOS5 and 6.
service redis-server restart
Change Memcached listening port
- Systemd
- Service
vi /lib/systemd/system/memcached.service
OPTIONS="-l 127.0.0.1" change to OPTIONS=""
systemctl daemon-reload
systemctl restart memcached
vi /etc/init.d/memcached
OPTIONS="-l 127.0.0.1" change to OPTIONS=""
chkconfig memcached on
service memcached restart